In order to qualify for funding or a loan from a bank, customers usually request credit ratings to be performed by a credit rating agency. Basically, banks require Credit Ratings to reduce the risk of default. At the present time, credit rating is required when getting a loan from Tk.30.00 lac and above.
Usually, Credit Rating is done for assessing the ability and willingness of the borrower that can be government, business entity, or individual to repay the loan or fund to fulfill its financial obligations within the set period.
You may like also: What are the documents required for SME loan?
In Our country, there are a number of credit rating agencies, who provide credit ratings for a reasonable fee. A renewal will be carried out every year. Before sanctioning loans, most banks verify the credit capacity and credit history of prospective borrowers through credit rating agencies on behalf of the applicants/borrowers.
What is Credit rating:
It we are trying to define credit rating in formative way then we can define credit rating as;
“Credit Rating is the process of way of identifying customer credit worthiness, ability to repay, financial strength for future funding as well as willingness to repay the existing one”.
The credit rating represents an evaluation of a credit rating agency of the qualitative and quantitative information for the prospective customer, including information provided by the prospective customer and other non-public information obtained by the credit rating agency’s analysts. (Wikipedia)
Purpose of Credit Rating:
From the definition it is quite clear that the purpose of Credit Rating is to assessing the ability, credit worthiness, financial strength of the applicant for funding as well as reduce the risk of banks for funding a faulty entity.
How is Credit Rating Done?
Each credit rating agency employs a different procedure for doing credit ratings. There are, however, some general steps that each agency follows. Let us have a brief look on the same.
- First of they collect some basic documents of customer to identify the customer i.e., 1) NID of the customer, 2) Trade License of Proprietor (in case of business entity), 3) Tin, 4) Financial Statement and income statement, 5) Insurance documents, 6) liability details, 8) IRC / ERC (if any), 9) Factory License or Business membership certificate if any, 10) Client loan application letter.
- Many credit rating agencies have their own data bank or data store where they maintain client wise details. With every passing loan enquiry, they keep updating their details.
- Agencies have their own team of credit analyst. They collect the required information & analyze the same. They also prepare score sheets & follow their own check lists.
- They also contact the applicant as and when required, discuss the various questionnaires they have.
- They may also visit the premises of the client to further verify the credit worthiness.
- In their rating procedural part, they analyze both financial characteristics & operational characteristics of any going concern.
- Not just qualitative factory, they also give due importance to qualitative factors & also reviews legal factors.
- Once, the rating data is collected, they deeply analyze each & every perspective of it & on the basis of this, final credit rating is determined.
- Any defaults made by the client in the previous years, are to be mentioned in the report which will lead our client towards a score which will indicate a higher risk.
- After completion of data collection and analysis, a summary of the rating will be communicated with the customer & after finalization, communicated to him & the concerned bank.
Credit Rating Scales and Definition
Credit Rating scale is the deciding factor on whether a borrower does or does not receive the applied loan facility or renewed the existing one. For SME rating Banks are allowing Risk Weighted Asset 60%(SME-3) for allowing loans. Banks have to keep lower provisions for the loan which possessed lower Risk-Weighted Assets.
Commonly Practiced Rating Scales and their definitions are given below;
For Long Term Credit Ratings
Rating Scale | Definition |
AAA | Excellent quality, offering the highest safety for timely servicing of financial obligations. Such institutions carry minimum risk |
AA+, AA, AA- | Very strong capacity for timely servicing of financial obligations offering high safety. Such institutions carry very low risk. |
A+, A, A- | Strong capacity for timely servicing of financial obligations offering adequate safety. Such institutions carry low credit risk. |
BBB+, BBB, BBB- | Adequate capacity for timely servicing of financial obligations offering moderate safety. The rating category denotes a moderate credit risk. However, changes in circumstances or economic conditions are more likely to affect the capacity for timely servicing of financial obligations. |
BB+, BB, BB- | Inadequate safety for timely servicing of financial obligations. Such institutions carry high credit risk. The entity remains more vulnerable to adverse economic changes over time. |
B+, B, B- | Low safety for timely servicing of financial obligations. |
CCC, CC, C | Very high risk for timely servicing of financial obligations. |
D | Entities with this rating are in the lowest category. They are either in default or likely to be in default soon. |
For Short-Term Credit Ratings
Rating Scale | Definition |
ST-1 | Strongest capacity for timely payment of financial commitments and carry the lowest credit risk. |
ST-2 | Strong capacity for timely payment of financial commitments and carrying the lowest credit risk |
ST-3 | Satisfactory capacity for timely payment of financial commitments and carry very low credit risk. |
ST-4 | Moderate capacity for timely payment of financial commitments and carry Moderate credit risk |
ST-5 | Uncertain capacity for timely payment of financial commitments and carrying high credit risk. |
ST-6 | Indicates actual or inherent payment default. |
Credit Rating Scale Mapped with Bangladesh Bank’s Rating Grade:
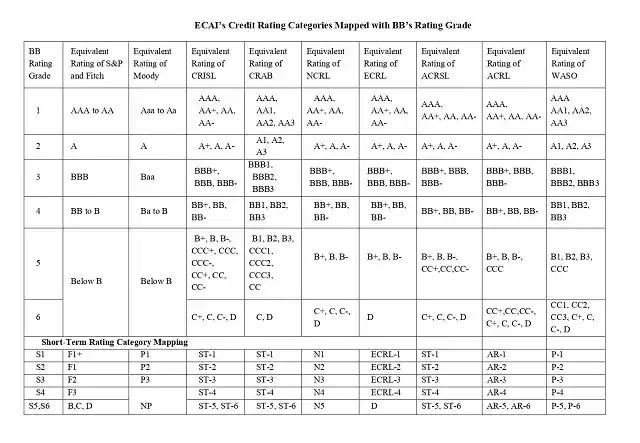





The Credit Rating provides a reasonable certainty about the applicant. If the rating is in marks, then depending upon their criteria, the better your credit rating, the better the terms of the loan. On the other hand, if your credit rating is poor, the bank may even reject your request for a loan.


