There are a number of ways, mediums and instruments for financial transactions and payment for purchases like mobile banking, internet banking, cards etc. But still cheque is the basic instrument for bank transactions. For that, it is important for us to know about the elements of a Bank cheque to ensure that the cheque is properly written before it placed either on bank or any person. Otherwise, you have to face hazards at the time of withdrawing money or mitigating your financial liabilities through cheque. When we try to write a cheque, several questions come to our minds. Like;
1) How to write a Bank Cheque?
2) Where to write the date on the cheque?
3) How to write the amount in the cheque?
4) Where to put a signature on the cheque?
5) Where to write the name of the bearer on the cheque?
And so, I will try to ease this problem or hesitation through my writing.
First of all, we try to know about parts of a cheque by the following sample cheque.
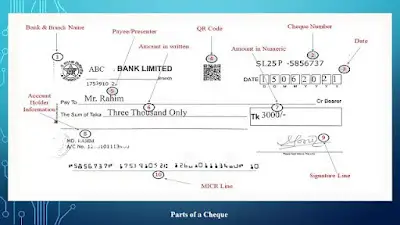
01. Bank & Branch Name: Here you can find the bank and Branch name along with Branch Routing number. It is an important element of a cheque. Routing number mostly used for making EFT (Electronic Fund Transfer) transactions.
02. Cheque Number: Usually there you find 5-12 numbers along with a letter which helps to track your cheque at the time of making a transaction. Every page of a cheque book contains a unique number for tracking cheques.
03. Date: In this box the cheque placed date will be written clearly. Normally we are practicing to write a date which is valid for 180 days from the written date. After 180 days this cheque will be void. It is also to be mentioned that you cannot place the cheque before the date written on the cheque.
Read Also: Is the Account payee cheque really safe? Best way to write account payee cheque.
04. QR Code: This QR code contains Account holder’s account details. Anyone can get it by scanning it through a QR code scanner. This feature is used by most of the banks for controlling cheque fraud.
05. Payee: In this area the recipient name of the cheque has to be written to whom the money is going to be paid; it can either be a person or a company. In our country we practiced to write ‘self’ if the account holder is the presenter of the cheque.

06. The Amount in written: The amount which is the account holder willing to pay or withdraw is to be written here in words clearly. This part is mostly acceptable to the bank authority if the numeric part is unclear.
07. Numeric amount box: Here the amount which is the account holder willing to pay or withdraw is to be written in numbers clearly. The amount in written and the amount in number must be the same.
08. Account Holder Information: This area contains the account holder’s name along with a 13-18-digit account number. This area is printed by the bank now.
09. Signature Line: This is a security feature that validates the cheque signing by the account holder according to the sign which is preserved by the bank at the time of account opening.
10. MICR line: It contains magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) data like cheque number, routing number, account number, transaction code that is easily read by machines. This data is important for the BACH (Bangladesh Automated Clearing House) process now.

How to Write a Bank Cheque or Cutting a Bank Cheque?
I think we have learned about different parts of a cheque, now we are ready to write a cheque. Usually we have to fill up those parts which are called material parts in banking language. I am here trying to demonstrate how to write a cheque by using this sample cheque;

1. Date Box:Usually every bank uses the dd/mm/year format for date. Here first two boxes for date, next two for month and the last four for the year.
2. Payee: Here must mention the name of the cheque presenter. If the account holder himself is the presenter the word ‘Self’ can be written. If the account holder specifies the presenter then the name of the presenter should be written in the “Pay to” line he/she has to cut the word BEARER(This cheque is called in banking “ORDER CHEQUE”) otherwise anyone except the mentioned name can withdraw this cheque.

3. Amount in written: Required amount for withdrawal must be written in words here.
4. Amount in Numeric: Withdraw amount is to be written in numbers clearly.
5. Signature line: Account holder must put his signature here which is recorded in bank at the time of account opening.
If any of this material part of the cheque is missing or makes mistakes in filling, bank authority can reject this cheque. But more or less every bank is practicing that, if any mistake occurs in the material part of the cheque account holder can validate it by countersigning where the mistake is done. Counter signs may be done more than one according to the number of mistakes made.
Back part of the cheque:

On the backside of the cheque at the top says “Endorse Check Here.” Here the presenter will sign two times. For account transfer account numbers may be written here to make sure the money goes where it should.
Under the endorsement line is a note that “Do not write, stamp or sign below this line.” That space is for the bank.
Bank/Branch First Deposit and Area of Endorsement these two are also used by bank officials for collection from another bank cheque.

In our country cheques written in English or Bangla both are accepted. But mixed languages are strictly prohibited. Account holders are supposed to use any one language to fill up the cheque.
I think from reading this content anyone can write a cheque more consciously and without any mistakes.
FAQs:
01. Is mixed Language acceptable in writing a Bank Cheque?
No. Banks are allowing anyone to write either Bangla or English language for writing a cheque. Mixed languages sometimes cause confusion in amount written and amount in number.
02. How to transfer a Cheque to another bank account?
Just write down the beneficiary account title with the number in the ‘Pay to’ line and make a Crossing sign at the top corner of the cheque as a sample cheque shown below.
03. What are the types of Bank cheques?
i) Self Cheque.
ii) Bearer Cheque.
iii) Order Cheque.
iv) Crossed Cheque.
v) Open cheque.
vi) Post-Dated Cheque.
vii) Stale Cheque.
04. What is the validity period of a cheque?
In Bangladesh, a cheque is valid for 180 days from the date of the issuance of the cheque. After 180 days it will be called a stale cheque.



